Yaml
works on helm v3.9.2
Project
Reserved for future.
Version
Helmwave will check current version and project version.
In the future it is planned to be used for major compatibility.
Registries[]
| field | required | type | default |
|---|---|---|---|
| host | ✅ | string | "" |
| username | string | "" | |
| password | string | "" |
Repositories[]
| field | required | type | default |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | ✅ | string | "" |
| url | ✅ | url | "" |
| username | 🙅 | string | "" |
| password | 🙅 | string | "" |
| certfile | 🙅 | string | "" |
| keyfile | 🙅 | string | "" |
| cafile | 🙅 | string | "" |
| insecureskiptlsverify | 🙅 | bool | false |
| force | 🙅 | bool | false |
name
Local name alias
url
URL for chart repository
force
Don't skip if repository exists.
Releases[]
Almost all options that are here are native helm options
| field | required | type | default | helmwave build |
helmwave up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | ✅ | string | "" | ✅ | ✅ |
| namespace | ✅ | string | "" | ✅ | ✅ |
| chart.name | ✅ | string | "" | ✅ | ✅ |
| chart.username | 🙅 | string | "" | ||
| chart.password | 🙅 | string | "" | ||
| chart.certfile | 🙅 | string | "" | ||
| chart.keyfile | 🙅 | string | "" | ||
| chart.cafile | 🙅 | string | "" | ||
| chart.insecureskiptlsverify | 🙅 | bool | false | ||
| description | 🙅 | string | "" | ||
| depends_on | 🙅 | array | [] | ✅ | |
| allow_failure | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| values | 🙅 | array | [] | ✅ | ✅ |
| tags | 🙅 | array | [] | ✅ | |
| store | 🙅 | object | {} | ✅ | |
| timeout | 🙅 | interval | 0s | ✅ | |
| max_history | 🙅 | int | 0 | ✅ | |
| create_namespace | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| reset_values | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| recreate | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| force | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| atomic | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| cleanup_on_fail | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| subnotes | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| disable_hooks | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| disable_open_api_validation | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| wait_for_jobs | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| wait | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| skip_crds | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| devel | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ | |
| reuse_values | 🙅 | bool | false | ✅ |
🗳️ Store
It allows to pass your custom fields from
helmwave.ymlto values.
It works when you call $ helmwave build
🔖 Tags
It allows you to choose releases for build
It works with next options when you call $ helmwave build:
--tags value, -t value It allows you choose releases for build. Example: -t tag1 -t tag3,tag4 [$HELMWAVE_TAGS]
--match-all-tags Match all provided tags (default: false) [$HELMWAVE_MATCH_ALL_TAGS]
Matching with tags
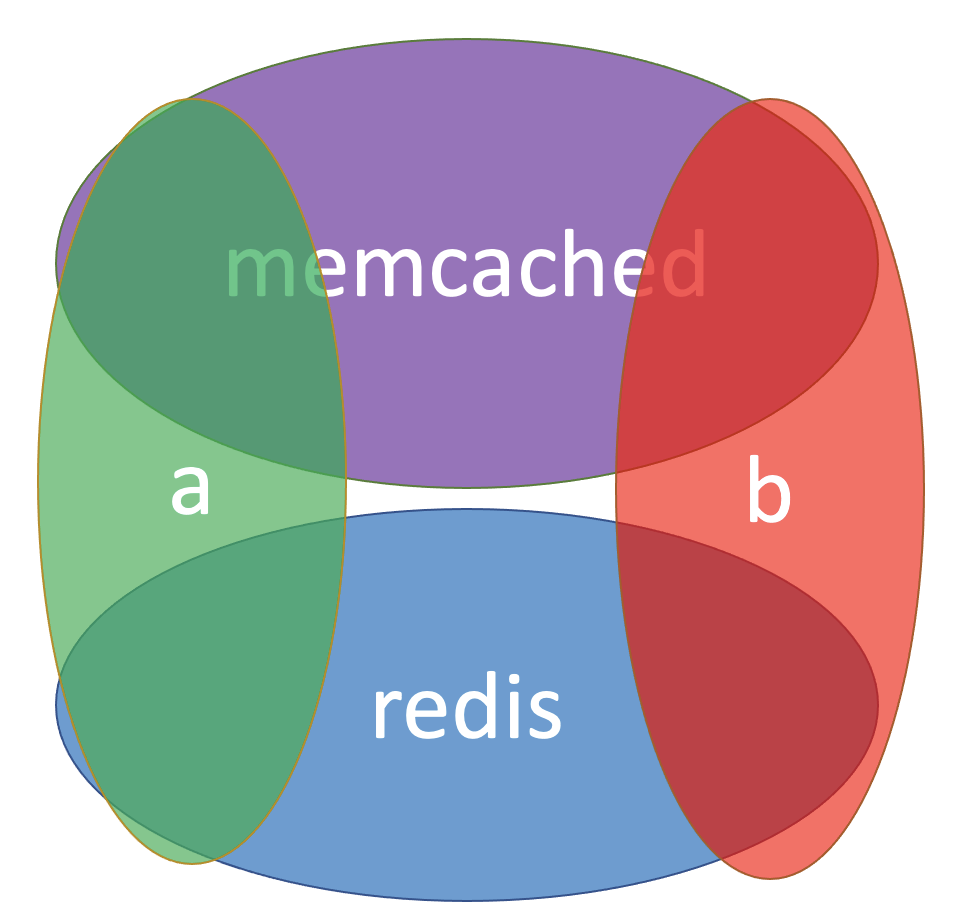
Suppose we have next helmwave.yml with 4 releases.
- redis-a
- redis-b
- memcached-a
- memcached-b
repositories:
- name: bitnami
url: https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
releases:
- name: redis-a
namespace: test
chart:
name: bitnami/redis
tags:
- a
- redis
- name: redis-b
namespace: test
chart:
name: bitnami/redis
tags:
- b
- redis
- name: memcached-a
namespace: test
chart:
name: bitnami/redis
tags:
- a
- memcached
- name: memcached-b
namespace: test
chart:
name: bitnami/memcached
tags:
- b
- memcached
Match all redis
helmwave build -t redis
[🙃 aka INFO]: 🏗 Plan
releases:
- redis-a@test
- redis-b@test
Match the group a
helmwave build -t a
[🙃 aka INFO]: 🏗 Plan
releases:
- redis-a@test
- memcached-a@test
Match multiply group.
If you know SQL. It looks like that:
SELECT * FROM releases WHERE tag = "redis" OR tag = "a"
helmwave build -t redis -t a
[🙃 aka INFO]: 🏗 Plan
releases:
- redis-a@test
- redis-b@test
- memcached-a@test
All that was above, we used the logical OR operator.
If you need strongly logic with AND you should use --match-all-tags flag.
This flag changes logic for query releases.
If you know SQL. It looks like that:
SELECT * FROM releases WHERE tag = "redis" AND tag = "a"
helmwave build -t redis -t a --match-all-tags
[🙃 aka INFO]: 🏗 Plan
releases:
- redis-a@test
depends_on & allow_failure
It allows waiting releases
It works when you call $ helmwave up
Example for 3-tier application
Your helmwave.yml will
releases:
- name: frontend
depends_on: backend@test
namespace: test
- name: backend
depends_on: db@test
namespace: test
- name: db
allow_failure: false
namespace: test
When allow_failure is set true. It allows the installation to proceed.
name
Release name
I hope you know what it is.
namespace
Kubernetes namespace
create_namespace
if
trueHelmwave will create the release namespace if not present
timeout
time to wait for any individual Kubernetes operation